Hydrotechnology, the innovative application of engineering and technology to water systems, is transforming how we generate, store, and manage energy. As the world shifts towards sustainable solutions, hydrotechnology is playing a pivotal role in integrating water and energy systems, enhancing efficiency, and supporting the transition to a low-carbon future.
What Is Hydrotechnology?
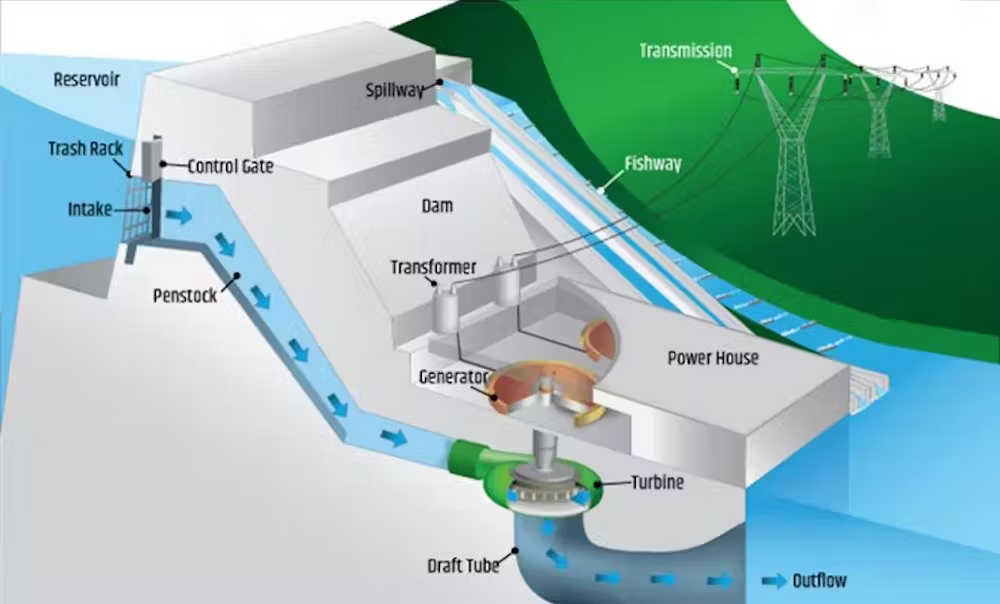
Hydrotechnology encompasses a range of technologies that harness the power of water for various applications, including energy generation, water purification, and environmental management. These technologies are crucial in addressing global challenges such as water scarcity, energy demand, and climate change.
Key Hydrotechnology Innovations
1. Pumped-Storage Hydroelectricity (PSH)
PSH is a well-established method of storing energy by using surplus electricity to pump water from a lower reservoir to a higher one. During peak demand, the stored water is released to generate electricity, acting as a large-scale battery. This technology is essential for balancing the grid and integrating renewable energy sources like wind and solar. Financial Times+2PCI+2Wikipedia+2
2. Floating Solar Panels
Floating solar, or floatovoltaics, involves installing solar panels on bodies of water such as reservoirs and lakes. These systems offer several advantages, including reduced land use, improved efficiency due to cooling effects from water, and the potential to reduce water evaporation. They are particularly beneficial in regions eco park gate no 2 land availability. Wikipedia
3. Geothermal Desalination
Geothermal desalination utilizes geothermal energy to power the process of converting seawater into freshwater. This method is energy-efficient and environmentally friendly, providing a sustainable solution for regions facing freshwater shortages. Wikipedia
Global Impact and Future Outlook
Hydrotechnology is not only enhancing energy efficiency but also contributing to environmental conservation and economic development. For instance, China’s approval of the world’s largest hydropower dam on the Yarlung Zangbo River aims to produce an estimated 300 billion kilowatt-hours of electricity annually, supporting the nation’s carbon neutrality goals. Reuters




Leave a Reply